Hearty, healthy, versatile
Hemp is one of the oldest, heartiest and most versatile plants on earth. It has been an important source of fibres, food and medicine throughout history. The industrial strain, known as cannabis sativa, produces fiber, oil and seeds. The entire plant can be processed into a wide range of raw materials such as pulp, paper, fuel, resins and wax. In the construction industry, variously processed hemp is used as a main component in bricks, particle board, insulation, and hempcrete, a concrete-like mixture that can be plastered or sprayed onto interior and exterior walls.
Sun-loving, naturally
Hemp uses sunlight more efficiently than most other plants, and therefore grows dense and vigorously, making it generally free of weeds, which fail under the canopy of a hemp field. It is also naturally resistant to pests, so rarely needs chemical treatment. Hemp limits topsoil erosion and its resultant water pollution, while its roots supply nitrogen and other nutrients to the soil and reduce ground water salinity. From a soil management perspective, hemp is perfect as a rotation crop because it replenishes the fields in which it is grown. It is especially complementary in rotation with wheat or soybean.
From the 28th Century B.C.
Hemp has been grown in almost all European, Asian, North and South American countries throughout history, and served as an important raw material for making ropes, canvas, textiles, paper and oil products. The first rope in recorded history was twisted from hemp in China in the 28th century B.C., with hemp-based paper and clothing dating to about the same period. In the pinnacle of sailing during the 17th century, Europe’s hemp industry had a heyday making sails rigging, ropes, nets, flags, and even seamen’s uniforms for national fleets.
To Hemp Today . . .
A growing number of organizations promote hemp for industrial use, expanding science and research and binding industry players together. Of course, they recognize hemp’s vast potential across a number of vertical markets. They know the ecological and other natural advantages of hemp-based products; and they recognize hemp’s potential to help meet the carbon reduction goals of countries around the globe. Area-wide hemp farming combined with local processing and production factories also holds great promise to contribute to rural economies, and such schemes are supported by more and more government programs.
What can hemp be?
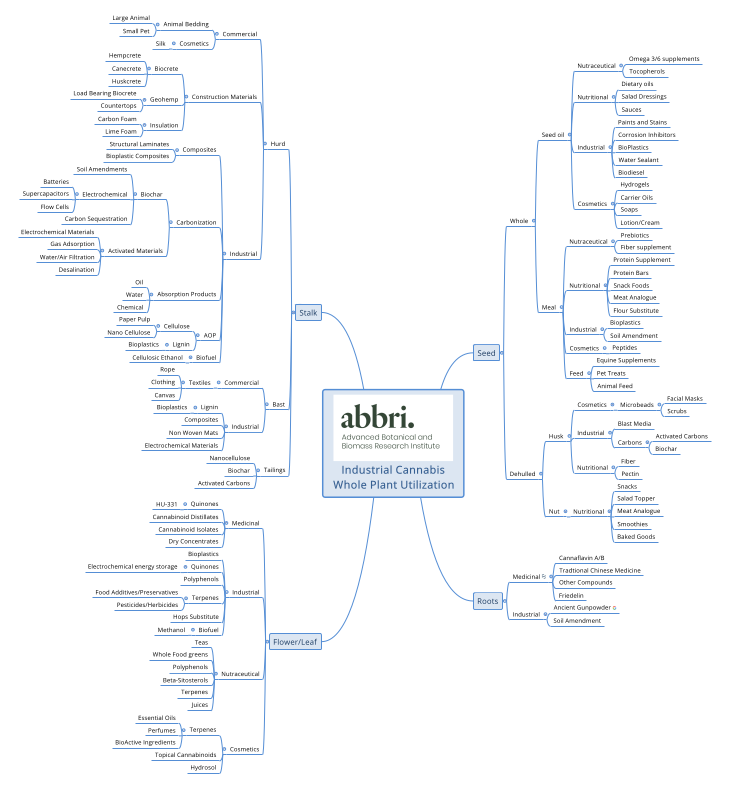
Here’s a look at the wide, wide range of applications for industrial hemp:
Building materials
Hempcrete – Sustainable mainly because it is made from a renewable resource, hempcrete is a versatile building material that offers a range of advantages over conventional materials such as concrete, brick, and wood. Made from a mixture of hemp hurds (“shivs,” or “shives”), the woody core of the hemp plant’s stem, mixed with lime and water, hempcrete can be used for walls, floors, and roofs. Hempcrete is used to create walls by infilling formed framing, and is also fashioned into pre-formed wall sections, blocks and bricks.
Hemp bast fiber insulation – Hemp bast fiber insulation is made from the outside bast fibers from the hemp plant stalk, and is an eco-friendly and sustainable alternative to traditional insulation materials such as fiberglass, rock wool, or foam.The lightweight and highly insulating material that can be used in walls, roofs, and floors to help regulate temperature and sound. Hemp bast fiber insulation has several advantages over traditional insulation materials, including its renewable and biodegradable nature, its resistance to mold and pests, and its ability to absorb and release moisture, which can help regulate indoor humidity levels.
“Hempwood” – Hempwood is made from the hard inner core of the hemp stalk, and is a sustainable alternative to traditional hardwoods. The hemp stalk pieces are mixed with a non-toxic adhesive and pressed together under high pressure and heat to form dense, durable board material that can be cut, sanded, and stained like traditional hardwood. Hempwood is used in flooring and furniture, and even musical instruments.
Textiles
Hemp has been used for centuries to make textiles. The fibers from the outside of the hemp plant stalk are long, strong, and durable, making them ideal for spinning into textiles for clothing, upholstery, and linens.
While still a niche product compared to clothing made from synthetic or conventional materials, fashions produced from hemp textiles are gaining popularity due to the increasing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly clothing options.
Hemp fibers have unique properties that make them well-suited for clothing. Textiles from hemp fibers are strong and durable, and become softer with each wear and wash. Hemp is also naturally antibacterial, which makes it a great choice for activewear and other garments that need to withstand frequent use.
Hemp is biodegradable, so it won’t contribute to the accumulation of non-biodegradable waste in landfills.
Food
Rich in nutrients, hempseeds are a good source of essential protein, vitamins, and minerals, including vitamin E, magnesium, zinc, and iron. The hemp seed’s high level of the amino acid arginine can help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease. Hempseed also offers healthy fats and may help reduce cholesterol levels, and is a good source of both soluble and insoluble fiber, which can promote healthy digestion and help regulate blood sugar levels; it also contains several compounds that have anti-inflammatory effects, such as gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), which may help reduce inflammation in the body.
Hempseeds are versatile and can be used in many different foods, such as:
Smoothies and shakes: Hempseeds can be blended into smoothies and shakes to add a nutty flavor and a boost of protein and healthy fats.
Baked goods: Hempseeds can be added to bread, muffins, cookies, and other baked goods for a nutty texture and flavor.
Breakfast foods: Hempseeds can be sprinkled on top of oatmeal, yogurt, or cereal for added protein and nutrients.
Salads and grain bowls: Hempseeds can be used as a topping for salads and grain bowls for added texture and nutrients.
Snacks: Hempseeds can be roasted and seasoned to make a tasty and healthy snack.
Sauces and dips: Hempseeds can be blended into sauces and dips, such as hummus or pesto, for added flavor and nutrition.
Vegan protein powders: Hempseeds can be ground into a powder and used as a vegan protein source in protein powders and shakes.
Health & beauty
Hempseed oil is a popular ingredient in cosmetics and health & beauty products due to its moisturizing, anti-aging, and anti-inflammatory properties, which make it a versatile and beneficial ingredient for a wide range of applications for the skin, hair, and body:
Moisturizer: Hempseed oil is rich in essential fatty acids and is easily absorbed by the skin. It can be used as a natural moisturizer for the face and body, helping to keep skin soft, supple, and hydrated.
Soaps: Those moisturizing benefits also make hempseed oil an excellent basis for soaps.
Hair care: Hair care products such as shampoos and conditioners based on hempseed oil moisturize and nourish the hair, leaving it soft, shiny, and healthy.
Anti-aging: Hempseed oil contains antioxidants, which help to prevent and reduce the signs of aging, such as fine lines and wrinkles. It can be used in anti-aging creams, lotions, and serums to improve skin elasticity and firmness.
Acne treatment: Hempseed oil has anti-inflammatory properties that can help to reduce inflammation and redness associated with acne. It can also help to regulate oil production, making it a good ingredient in acne-fighting products.
Lip balm: Hempseed oil can be used in lip balms and lipsticks to moisturize and protect the lips from dryness and cracking.
Massage oil: Hempseed oil has a smooth, silky texture and is easily absorbed by the skin, making it an excellent massage oil.
Plastics & biocomposites
Bioplastics and other biocomposites based on hemp fibers can be used in a wide range of products, such as automotive parts, construction materials, packaging, and consumer goods. Biocomposites made with hemp fibers are a sustainable alternative to traditional composites made with synthetic fibers, which are often derived from non-renewable sources and can be difficult to recycle.
The hemp fibers reinforce bioplastics, making them stronger and more durable. The fibers can be used in various forms, including chopped, milled, or as a woven mat, and can be added to the polymer matrix through various manufacturing processes, such as extrusion, injection molding, and compression molding. Hemp can also be used as a filler in bioplastics.
Biodegradable plastics made from hemp can break down naturally over time, which can help to reduce the environmental impact of plastic waste.
Biochar
Industrial hemp has the potential to be a valuable input for the production of biochar, a form of charcoal that is produced from organic materials through a process called pyrolysis. The organic material is heated in the absence of oxygen, which creates a stable carbon-rich material that can be used for a variety of applications.
The use of industrial hemp as an input for biochar production has significant potential as a sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to both agriculture and carbon sequestration. And hemp’s potential to produce high biomass yields means it produces a lot of plant material per acre. And the hemp plant’s low lignin content, makes it well-suited for biochar production.
Biochar has many potential applications, including:
Agricultural soil improvement: Biochar can be mixed with soil to improve soil quality by increasing water retention, providing a source of slow-release nutrients, and improving soil structure.
Carbon sequestration: Biochar can store carbon in the soil for hundreds of years, helping to mitigate climate change.
Water treatment: Biochar can be used as a filter media to remove pollutants and contaminants from water.
Animal feed: Biochar can be added to animal feed to improve digestion and reduce the amount of methane produced by livestock.
Energy production: Biochar can be used as a fuel for electricity generation and heating.
Construction material: Biochar can be used as a building material for insulation and as a lightweight aggregate in concrete.
Environmental remediation: Biochar can be used to remediate contaminated soils by absorbing heavy metals and other toxins.
Horticulture: Biochar can be used as a growing medium for plants and as a component in potting soil.
Landscaping: Biochar can be used as a mulch to help retain moisture and suppress weed growth.
Biochar also has several potential high-tech applications:
Energy storage: Biochar has a high surface area and can be used as a material for energy storage, similar to batteries or supercapacitors.
Water filtration: Biochar has a porous structure that can be used for water filtration, helping to remove impurities and contaminants.
Bioplastics: Biochar can be used as a filler material in bioplastics, improving their strength and durability.
Catalysis: Biochar can be used as a catalyst for various chemical reactions, such as the production of biofuels or the synthesis of chemicals.
Construction materials: Biochar can be used as a component in building materials, such as concrete, to improve their strength and reduce their carbon footprint.
Other products
Paper – Hemp has been used for paper-making for centuries, and it was the primary material used for paper until the mid-1800s when wood pulp paper became more common. Hemp fibers can be processed to make high-quality paper that is both strong and durable. Because hemp requires fewer chemicals to process than traditional paper materials like wood pulp, it is considered to be more environmentally friendly. Hemp paper can be used for a variety of purposes, including sustainable packaging material, for fine art prints, stationary and cigarette papers. Hemp paper is fully biodegradable and does not contribute to the accumulation of waste in landfills.
Rope and twine – Hemp fibers have been used to make rope and twine for thousands of years, thanks to their strength and flexibility. Hemp and twine made from hemp are much stronger than those made from cotton or other natural fibers, meaning they can carry heavier loads. Also hemp fibers are naturally resistant to water – they won’t rot or weaken when exposed to moisture.
Animal bedding – Animal bedding made from hemp straw is well-suited for use with animals such as horses, cows, and other livestock. It provides a soft and comfortable bed for large animals, and is highly absorbent, which helps keep them clean and dry. In addition, hemp straw bedding has natural antimicrobial properties, which helps to reduce the risk of infection. Hemp straw is biodegradable and can be composted or used as fertilizer once it has been used as bedding.
Pet litter – Hemp straw can also be used as a litter for cats and other small animals. Small animal litter is made processed stalks that are cut into small pieces to create a soft and absorbent bedding material. Hemp straw litter is an eco-friendly alternative to traditional clay-based litters, which are often derived from non-renewable resources and can be harmful to the environment. Hemp straw litter is also free from dust and chemicals, making it a healthier option for both pets and their owners. Hemp straw litter can be disposed of in compost bins or used as garden mulch after it has been used.
Environmental benefits
The environmental benefits of industrial hemp make it a promising crop for sustainable agriculture and a valuable tool for addressing environmental challenges such as climate change, soil degradation, and biodiversity loss. Among the benefits of this versatile and sustainable crop:
Carbon sequestration: Fast-growing hemp absorbs large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, making it an effective tool for carbon sequestration. Studies have shown that hemp can sequester up to 15 tons of carbon dioxide per hectare per year.
Soil remediation: Hemp has deep roots that can help to aerate and loosen compacted soil, making it more suitable for other crops. Additionally, hemp is known for its ability to remove toxins and pollutants from soil, a process known as phytoremediation.
Reduced use of pesticides and herbicides: Hemp is naturally resistant to pests and diseases, which means that it requires fewer pesticides and herbicides than other crops. This can help to reduce the amount of harmful chemicals that are released into the environment.
Water conservation: Hemp requires less water than many other crops, making it a more sustainable choice in areas where water resources are limited.
Biodiversity: Hemp can be grown in rotation with other crops, which can help to promote biodiversity on agricultural lands. Additionally, hemp can be used to create habitats for wildlife, further supporting biodiversity.
Sustainable production: Hemp can be grown using organic and regenerative farming practices, which can help to reduce the environmental impact of agriculture and promote sustainability.
