The fiber and bio-energy sectors represent the best opportunities for industrial crops in Europe, according to a focus group survey among agriculture experts carried out by the European Commission (EC). Forty-two percent of respondents identified raw materials for fiber production as the “most likely use for industrial crops” while 32% ranked bio-energy as having the most potential.
The responses came from the EC’s Focus Group on Sustainable Industrial Crops in Europe, part of the European Innovation Partnership for Agriculture (EIP-AGRI) initiative. Experts in research, farmers, consultants and other industry professionals participated in the survey, which explores the outlook for non-food crops.
‘Most potential’
Hemp gets extensive treatment in a section of the report that looks at the comparative potential of 15 industrial crops for economic development, environmental and social impacts. A strong role in economic development is implied by hemp’s fit into a broad range of categories including pharmaceuticals, food supplements, cosmetics, bio-composites, energy, textiles, paper and construction materials.
“Hemp” is mentioned 183 times in the 121-page document, far more than any of the other crops analyzed: camelina, castor bean, cardoon, castor, cord grass, flax, giant reed, kenaf, miscanthus, switchgrass, sorghum, sugar beet, poplar, Virginia mallow, and willow.
“It’s clear this analysis shows hemp has the most potential among industrial crops in Europe,” said Hana Gabrielova, CEO at Czech-based Hempoint, who served as an expert in the focus group. “From its high score in different uses to its potential to clean heavy metals from soil, hemp is a perfect fit in the EU’s vision for agriculture and to support the Green Deal policy,” Gabrielova said. Green Deal is the EC’s initiative that aims to make Europe climate neutral by 2050.
It’s also food
“A great advantage of hemp among other industrial crops is that hemp does not create competition against food crops because hemp itself it can be a high-nutrition food,” said Gabrielova, whose company is a food grower, product developer and producer.
Most promising sectors for industrial crops
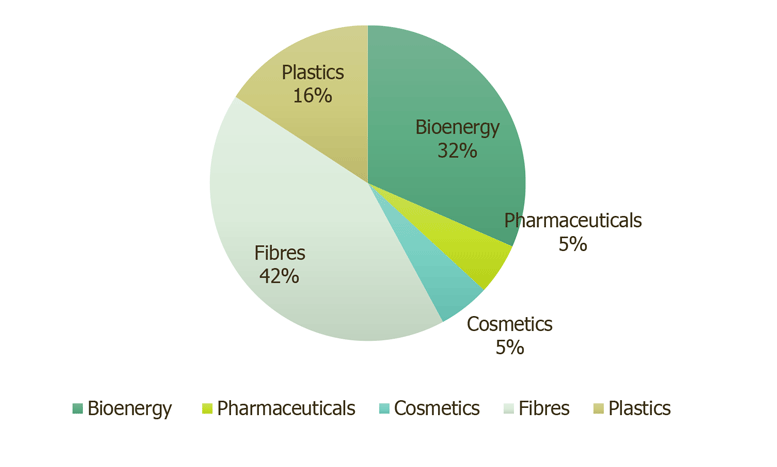
“Industrial crops can have many benefits including carbon sequestration, displacement of fossil fuels, improving profit margins for farmers and enhancing utilization of marginal and contaminated land,” according to the report, which suggests industrial crops can also help farmers in the transition to organic and sustainable farming.
“The use of industrial crops as sources of raw materials for traditionally petroleum-based products, like polymers and solvents, will facilitate a shift to more sustainable consumption of resources,” the authors write.
Search for cutting edge
The focus group was launched to advance cutting edge solutions for European agriculture through stakeholder collaboration. The group’s ultimate goals are to gather knowledge and document practical experience to foster industrial farming practices, and explore new market opportunities, business models and sustainable farming systems for industrial crops. The group’s work is part of the process that sets the basis for legislative text.
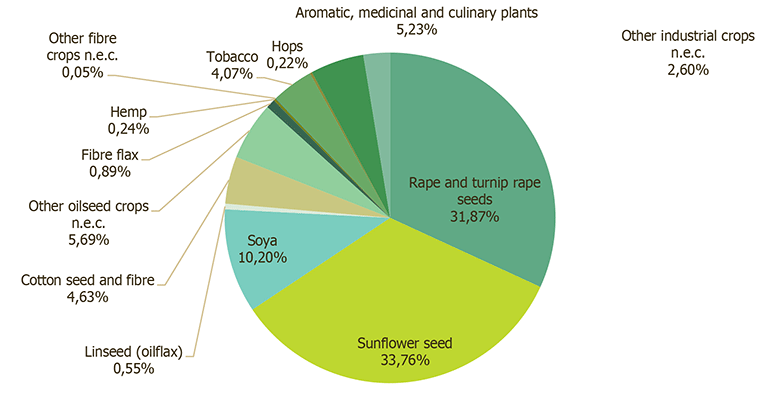
With total industrial crop farmland making up only 4.7% of fields in Europe (2016 census), hemp fields total only 0.24% of that small area, which is dominated by rapeseed (canola) (~32%) and sunflower seed (~34%). While that reflects the nascent status of industrial hemp in European agriculture, the versatile crop gets disproportional and highly promising analysis in the report, which clearly shows its potential to meet EIP-AGRI’s goals.
Total area cover for industrial crops in Europe (2016 census)
The challenges
While non-food crops have great potential, farmers suffer from “lack of confidence and experience in growing industrial crops,” the report observes, suggesting professional networks and cooperatives need to be established for knowledge exchange. Demonstration projects are needed which can “provide transparent business models for farmers and industry,” the report urged.
Five mini-papers that are part of the report address the following topics in-depth: “Understanding the sustainability aspects of Industrial Crops”; “Selected Value Chains for Industrial Crops”; “Market Opportunities for Multi-Purpose Crops in the EU”; “Industrial Crops for Marginal and Contaminated Lands, Intermediate Crops and Intercropping Strategies”; and “Review of Industrial Crops as part of Advisory, Research and Educational Programmes in Europe.”
Full report: EIP-AGRI Focus Group on Sustainable industrial crops

